So, let's talk about capital gains tax, shall we? It's one of those topics that can make your head spin, but don't worry, we're here to break it down for you in a way that's easy to digest. Whether you're a seasoned investor or just starting out, understanding capital gains tax is crucial if you want to maximize your returns and keep more of your hard-earned money. So, grab a coffee, get comfy, and let's dive in!
Now, I know what you're thinking. "Why do I even need to care about capital gains tax?" Well, my friend, if you've ever sold a stock, property, or any other asset for more than you paid for it, congratulations—you've just triggered a capital gain. And guess what? Uncle Sam wants his fair share. That's where capital gains tax comes in. It's basically the tax you pay on the profit you make from selling an asset.
But here's the thing: capital gains tax doesn't have to be this big, scary monster lurking in the shadows of your financial life. With a little knowledge and some smart planning, you can navigate it like a pro. So, whether you're looking to sell your first property or you're managing a massive investment portfolio, this guide has got your back.
Read also:Stephanie Rosenthal The Woman Revolutionizing The Art And Museum World
What Exactly Is Capital Gains Tax?
Alright, let's start with the basics. Capital gains tax is the tax you pay on the profit you make when you sell an asset. This could be anything from stocks and bonds to real estate or even precious metals. The key here is that it's only triggered when you sell the asset and realize the gain. So, if you're holding onto something, you're not liable for the tax—yet.
Now, there are two types of capital gains: short-term and long-term. Short-term capital gains apply to assets you've held for less than a year, and they're taxed at your ordinary income tax rate. Long-term capital gains, on the other hand, kick in when you've held an asset for more than a year. These are usually taxed at a lower rate, which is a nice little perk for those of us who like to play the long game.
Why Does Capital Gains Tax Matter?
Capital gains tax matters because it directly impacts your bottom line. Let's say you sell a property for a cool $500,000 profit. If you're in the higher tax brackets, that could mean a significant chunk of that profit goes straight to the IRS. But here's the kicker: with proper planning and strategy, you can minimize that tax burden and keep more of your money where it belongs—in your pocket.
Plus, understanding capital gains tax can help you make smarter investment decisions. For example, if you know that holding onto an asset for more than a year could save you thousands in taxes, you might be more inclined to take the long-term approach. It's all about playing the game smartly and making informed choices.
How Is Capital Gains Tax Calculated?
Calculating capital gains tax isn't rocket science, but it does require a bit of number crunching. Here's the basic formula: take the sale price of the asset, subtract the original purchase price (also known as your basis), and voila—you've got your capital gain. Easy peasy, right?
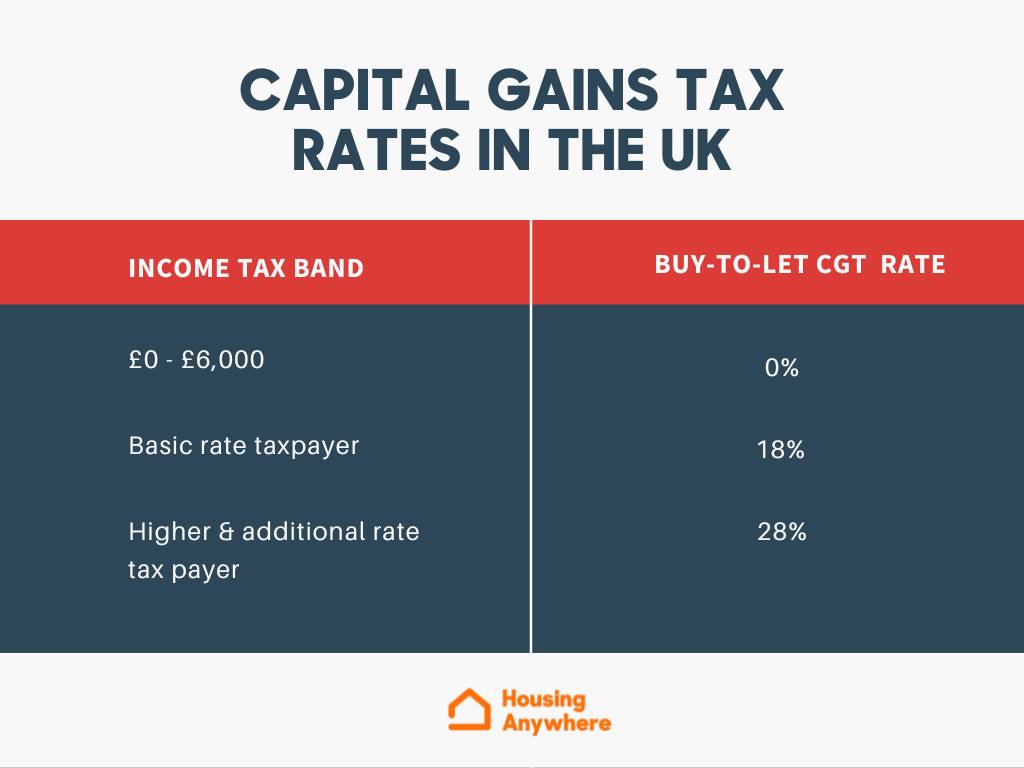
But wait, there's more. Depending on how long you've held the asset, you'll be subject to either short-term or long-term capital gains tax rates. Short-term rates are the same as your ordinary income tax rate, while long-term rates are generally lower. For most people, long-term capital gains tax rates are 0%, 15%, or 20%, depending on your income level.
Read also:River Russell Deary The Rising Star Shining Bright In The Entertainment World
- Short-term capital gains tax rate: Same as your ordinary income tax rate.
- Long-term capital gains tax rate: 0%, 15%, or 20%, depending on your income.
Now, here's where things can get a little tricky. There are also additional taxes to consider, like the Net Investment Income Tax (NIIT), which adds an extra 3.8% for high-income earners. But don't sweat it—we'll break all of this down in more detail later.
Factors That Affect Your Capital Gains Tax
Several factors can influence how much capital gains tax you owe. These include:
- How long you've held the asset: Short-term vs. long-term.
- Your income level: Higher income means higher tax rates.
- Type of asset: Some assets, like collectibles, are taxed at a flat rate of 28%.
- State taxes: Some states have their own capital gains tax rates, so be sure to check your local regulations.
It's important to keep all of these factors in mind when making investment decisions. For example, if you're in a lower tax bracket, you might want to consider selling assets sooner rather than later to take advantage of the lower rates. Or, if you're in a higher bracket, you might want to explore ways to defer or minimize your tax liability.
Who Pays Capital Gains Tax?
Not everyone is subject to capital gains tax, but if you're an investor or property owner, chances are it applies to you. Here's a quick rundown of who pays:
- Individuals: If you sell an asset for a profit, you're on the hook for capital gains tax.
- Businesses: Corporations and other business entities also pay capital gains tax on their profits.
- Trusts and Estates: These entities are also subject to capital gains tax, though the rates may differ.
Now, there are some exceptions. For example, if you sell your primary residence and meet certain criteria, you might be able to exclude up to $250,000 of the gain (or $500,000 if you're married filing jointly). That's a pretty sweet deal, if you ask me.
Exclusions and Deductions
Speaking of exclusions, there are several ways you can reduce your capital gains tax liability. Here are a few to keep in mind:
- Primary residence exclusion: As mentioned earlier, you can exclude up to $250,000 (or $500,000 for married couples) of the gain on the sale of your primary residence.
- Investment losses: If you have losses from other investments, you can use them to offset your capital gains.
- Charitable donations: Donating appreciated assets to charity can help you avoid paying capital gains tax altogether.
These exclusions and deductions can make a big difference in your overall tax bill, so it's worth exploring all of your options. And remember, it's always a good idea to consult with a tax professional to ensure you're taking full advantage of every opportunity.
Strategies to Minimize Capital Gains Tax
Now that we've covered the basics, let's talk about some strategies to help you minimize your capital gains tax. Here are a few ideas to get you started:
- Hold onto assets for longer: The longer you hold an asset, the more likely you are to qualify for the lower long-term capital gains tax rate.
- Time your sales: If you're in a lower tax bracket one year, it might make sense to sell assets then rather than in a higher-bracket year.
- Use tax-efficient accounts: Accounts like IRAs and 401(k)s can help you defer capital gains tax until retirement.
These strategies can save you thousands in taxes over time, so it's definitely worth putting in the effort to plan ahead. And hey, if you're not sure where to start, don't hesitate to reach out to a financial advisor or tax professional. They're there to help!
Investing in Tax-Friendly Assets
Another way to minimize capital gains tax is by investing in tax-friendly assets. Here are a few examples:
- Municipal bonds: These are often exempt from federal and state taxes.
- Index funds: These tend to have lower turnover rates, which means fewer capital gains distributions.
- ETFs: Exchange-traded funds can be more tax-efficient than traditional mutual funds.
By focusing on these types of investments, you can reduce your overall tax burden and keep more of your money working for you. It's all about making smart choices and planning for the future.
Real-World Examples of Capital Gains Tax
Let's take a look at a couple of real-world examples to see how capital gains tax works in practice.
Example 1: John buys a stock for $10,000 and sells it a year later for $15,000. His capital gain is $5,000. Since he held the stock for more than a year, he qualifies for the long-term capital gains tax rate. Depending on his income, he might pay 0%, 15%, or 20% on that gain.
Example 2: Sarah sells her primary residence for $500,000 after living there for two years. She originally bought the house for $300,000, so her gain is $200,000. However, since she qualifies for the primary residence exclusion, she can exclude up to $250,000 of the gain, meaning she owes no capital gains tax.
These examples illustrate how different factors can impact your capital gains tax liability. It's all about understanding the rules and making the most of the opportunities available to you.
Tips for Managing Capital Gains Tax
Here are a few final tips to help you manage your capital gains tax:
- Keep detailed records: Good record-keeping is essential for tracking your basis and calculating your gains.
- Consult a professional: A tax advisor or financial planner can help you navigate the complexities of capital gains tax.
- Stay informed: Tax laws can change, so it's important to stay up-to-date on the latest regulations and opportunities.
By following these tips, you'll be well-equipped to handle whatever the tax man throws your way. And who knows? You might even come out ahead.
Kesimpulan
Capital gains tax doesn't have to be this big, scary monster. With a little knowledge and some smart planning, you can navigate it like a pro and keep more of your money where it belongs—in your pocket. Remember, the key is to understand the rules, take advantage of exclusions and deductions, and make informed investment decisions.
So, what are you waiting for? Grab a pen and paper (or your favorite note-taking app) and start putting these strategies into action. And don't forget to share this article with your friends and family—because knowledge is power, and power is wealth. Now go out there and make it happen!
Call to Action
Got any questions about capital gains tax? Leave a comment below, and we'll do our best to help you out. And while you're at it, why not check out some of our other articles on personal finance and investing? There's always more to learn, and the more you know, the better off you'll be. Cheers to building wealth and achieving financial freedom!
Table of Contents:
- What Exactly Is Capital Gains Tax?
- Why Does Capital Gains Tax Matter?
- How Is Capital Gains Tax Calculated?
- Who Pays Capital Gains Tax?
- Strategies to Minimize Capital Gains Tax
- Real-World Examples of Capital Gains Tax
- Tips for Managing Capital Gains Tax
- Kesimpulan
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Capital-gain-2e9b43786c824dba8394bf73bd77f81e.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/capital_gains_tax.asp-Final-2add8822d04c4ea694805059d2a76b19.png)